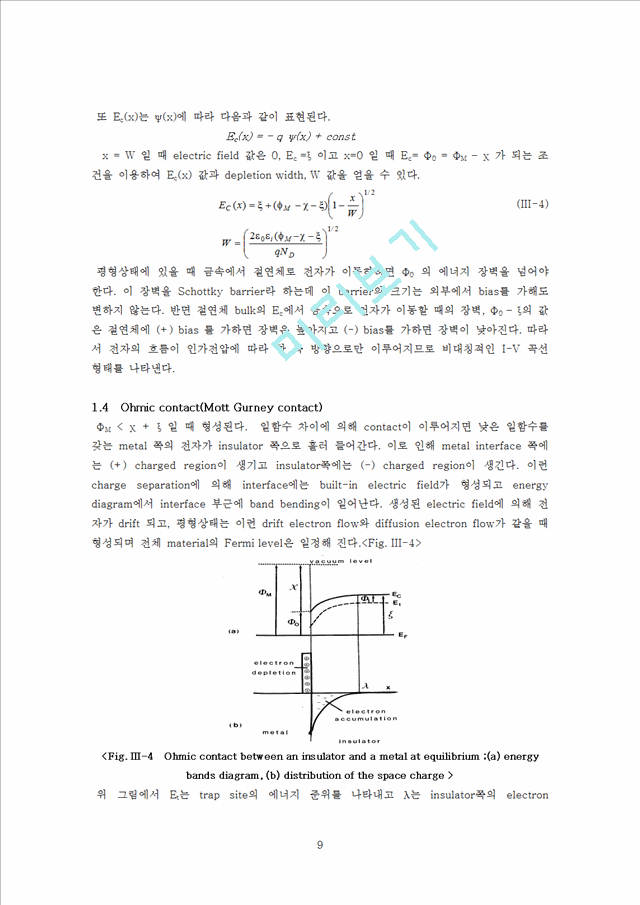
|
I Introduction
ь ььЌыЃ, эЙэ ыАыьВД ьЌыЃьь ь ъИАь эЙьБ(electrical properties)ь ьЁАьЌэы ъВь ьыЙэ ьЄьэыЄ. ьДыА electrical propertyыЅМ ьИЁь эы ыАЉыВ ьЄь I-V ьИЁь ьД ьыыА, ьДы ьАыІЌъА ьэы ьЌыЃь эЙь ь ьь эы Є ьЃМьь ы ьДь ыАьэьЌ ыэыы ь ыЅыЅМ ьИЁь эЈьМыЁьЈ ъЗИ ьЌыЃь ыЙь эьДыМы ъА ыьЄь ыЅ(leakage current) эЙьБ, ъЗИыІЌъГ эъДД ь ь (breakdown voltage) ыБь ьИЁь э ь ьыЄ. ьДыА ьИЁь ъАь э ыыЁ ьАыІЌъА ьІьАЉэ ь ь ьВД ыАыЇь эЙьБь эъАэ ь ьъВ ыыЄ.
ьДыА I-V ьИЁь ь ьДэД эъИАьэД ыЈМь ьМыАь ьИ ыАыьВД ьЌыЃььь carrier transport phenomenaь ыэДь ъАыЕэ ььыГИ ыЄь ыьВД-ыЖыьВД ьЌьДь contactьМыЁыЖэА ь ыЅъА эыЅДы ыЉьЛЄыьІь ьДэДыЅМ эЕэД voltageыЅМ эы ЄьЄ ы ьДыЄ ыАьь эЕэД ь ыЅъА ь ь ьВД ыАыЇь эЕэД эыЅДъВ ыыьЇ ььыГДъВ ыЄ. ъЗИыІЌъГ ыЇьЇыЇьМыЁ ьЄь ьИЁь ьь ьЌьЉыы ьЅыЙь ыэД ъАыЕэ ьъАэыыЁ эъВ ыЄ.
II. Carrier Transport Phenomena in general materials
ьЌыЃьь ь ьь ь ъГЕ(hole)ъГМ ъАь charged particleь net flowь ьэД ь ыЅъА эыЅИыЄ. ьДыА эыІ(flow)ь тtransportтыМ эыыА ы ъАьЇ ъИАыГИь ьИ transport mechanismьМыЁы diffusionъГМ driftъА ьыЄ. ь ьы charged particleь ыыьАЈь ьэ transportьДъГ эьы ь ъИАьЅь ьэ charged particleь эыІь ыэыИыЄ. ьДьИь ьЈыьАЈь ьэ flowы ьь ь ььМы sizeъА ьььЇьыЁ ъЗИ эЈъГМы ь ьДьЇыЄ. ьДыА carrier transport phenomenaы ыЄьь ьЄыЊ
ы ьЌыЃь I-V эЙьБь ьДэДэыыА ъИАыГИьД ыыЄ.
.
1. Carrier drift
ыЇьН ьЌыЃь ь ъИАьЅь ъАэыЉД ь ьь holeь ьД ь тІ(ьыЕ)
|
e mobilityыМъГ эыЄ.
ыАыМь ьь ь(II-2)ь (II-4)ыЁ ыЖэА ыЄь ъДъГъА ьБыІНэыЄ.
(II-5)
ыЇьАЌъАьЇыЁ ь ьь ыэДьы ы ъАь ъДъГъА ьБыІНэыЄ.
(II-6)
ыЙыЁ ь ьъА ь ъИАьЅь ыАыыЁ ььЇьДьЇыЇ ьМыАь ьМыЁ ь ьь drift currentы ь ъИАьЅъГМ ъАь ыАЉэЅьМыЁ ыГИыЄ.
ыАыМь ь ьВД ь ьь holeь ьэ total drift current densityы ь ь, hole ъАъАь drift current densityь эЉъГМ ъАыЄ.
(II-7)
ьЌъИАь Яы conductivityыЅМ ыэыИыЄ.